- TEL:
- +81-3-5462-4831
- FAX:
- +81-3-5462-4835
※9:00-17:40 Mon.-Fri. (JST)


Alex Horánszky, Bachuki Shashikadze, Radwa Elkhateib, Salvo Danilo Lombardo,
Federica Lamberto, Melinda Zana, Jörg Menche, Thomas Fröhlich and András Dinnyés.
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11:1236243. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2023.1236243
Copyright: © 2023 Horánszky, Shashikadze, Elkhateib, Lombardo, Lamberto, Zana, Menche, Fröhlich and Dinnyés.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY).
Bisphenol A (BPA) is commonly used as a raw material for plastics and adhesives, but it is also known to bind weakly to estrogen (female hormone) receptors. As an endocrine disruptor, tolerable daily intake (TDI) for bisphenol A is 50 µg/kg/day in Japan, and BPA elution test regulation for polycarbonate containers is 2.5 ppm (about 11 µM) or less under the Japan Food Sanitation Act. Recently, however, it has been reported that even extremely low doses have adverse effects on brain and organ development.
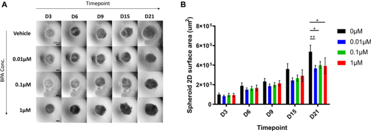
In this study, the effects of BPA on neural stem cells (NSCs) were evaluated in a human iPS-derived 3D neural stem cell model: BPA-treated NSC spheroids were smaller in size, suggesting proliferation inhibition by BPA. Proteomic analysis showed that BPA treatment reduced Wnt-8b in human NSC model, confirming that BPA can induce canonical Wnt alterations in a human NSC model for the first time. In addition, decreases in GAP43, GPC4 and TPPP3, which are involved in the regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway, and an increase in FABP7, which suggests a transition to radial-glial progenitor cells of BPA-treated NSCs, were observed. These findings indicate a possible molecular mechanism by which BPA may affect the proliferative differentiation of NSCs.
PrimeSurface™ 96V plates were used to induce differentiation of human neural stem cells from human iPS cells.
| Cell | : | hiPS cells; 10,000 cells/well |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | : | neural induction medium, partial medium exchange every 3 days |
| BPA treatment | : | exposure to 0-1µM BPA during differentiation induction |
[Results]
The cell viability and LDH assays were performed on BPA-exposed and control NSC spheroids. Mitochondria and ROS levels were also compared. Although spheroids were smaller in culture Day21 compared to controls, there was no significant difference in cell viability suggesting that a molecular mechanism was involved in the difference.
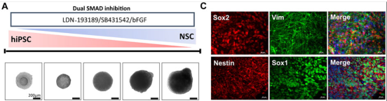
[Fig.1] Characterization of hiPSC-derived NSCs
[Fig.4] Spheroid size and growth curves under BPA treatment during the neural induction process
| Cat # | Product name | Well | Color | Bottom design | Well Vol | Package |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS-9096VZ | PrimeSurface™ 96V | 96 | Transparent | V bottom | 300 μL | Individual packaging 20 plates per case |
Remark