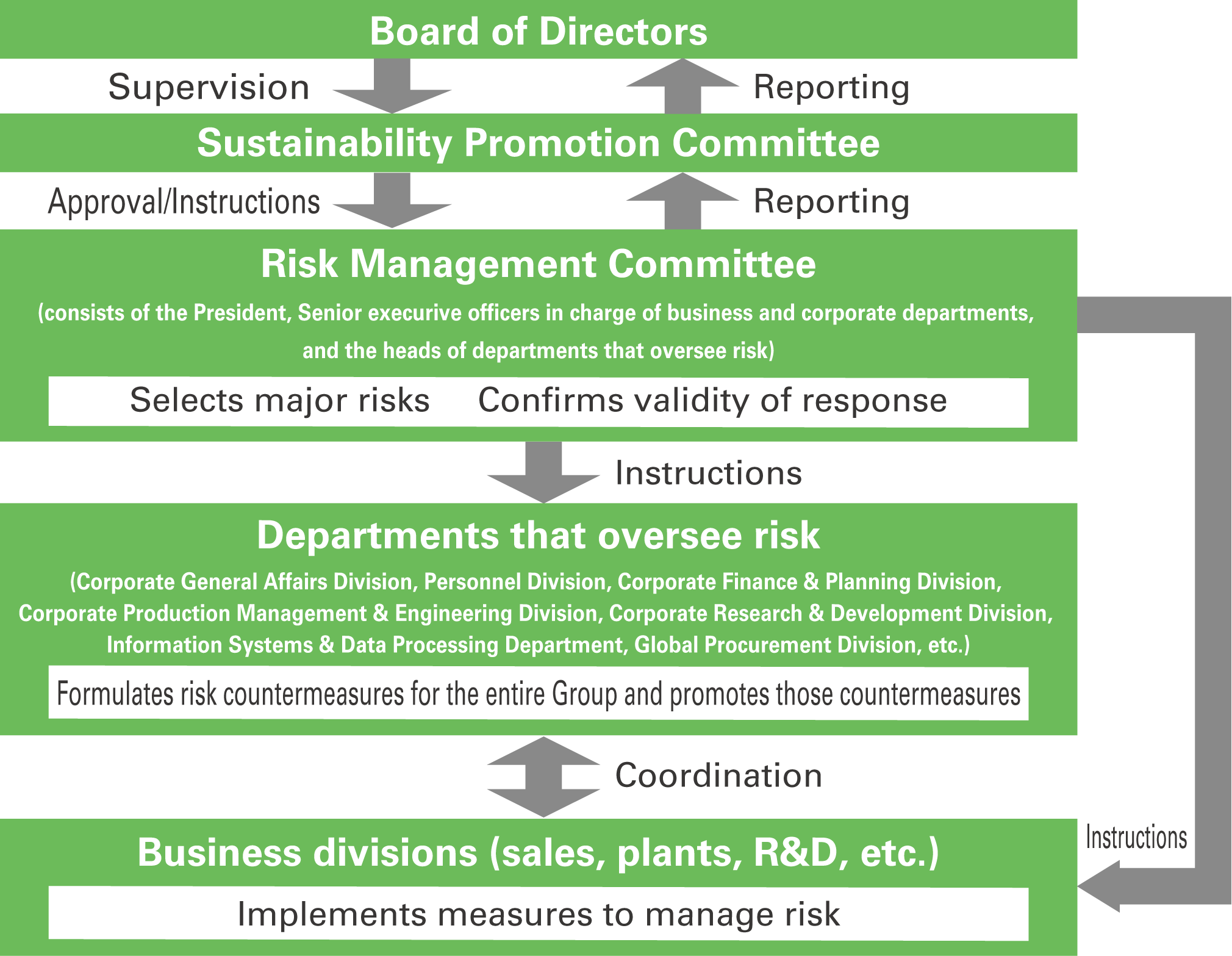
Risk Management Structure
Our Group’s risk management structure is described below.
● Sustainability Promotion Committee
We have established the Sustainability Promotion Committee as the parent body for conducting our Group’s sustainability activities on a continuous, Group-wide basis. It approves the policies, plans, results, items, and figures to be published externally by the Risk Management Committee, which is a subordinate comittee, and reports that information to the Board of Directors.
● Risk Management Committee
The Committee identifies major risks that could have a serious impact on our business performance, confirms the validity of response measures to major risks, and gives instructions on what additional measures should be considered to our departments that oversee risk and each department. The members of the Risk Management Committee consist of the President, Senior executive officers in charge of business and corporate departments, and the heads of departments that oversee risk.
For information about activities of the “Risk Management Committee,” see “Detailed Data Related to Sustainability (Governance) > Risk Management.”
● Divisions that oversee risk
When it comes to risk oversight, the departments that oversee risk draft and promote response measures for our Group as a whole by coordinating with each business department. These divisions that oversee risk include the Corporate General Affairs Division, Personnel Division, Corporate Finance & Planning Division, Corporate Production Management & Engineering Division, Corporate Research & Development Division, IT Promotion Division, and Global Procurement Division.
● Each business department
As part of their original business operations, the Group’s sales departments, factories, R&D departments, and other business units take various measures to properly manage the risks associated with the execution of their own business operations.
In addition to the above, the Group has established a corporate governance system and has developed and operated an internal control system, including risk management as described in “Corporate Governance.”
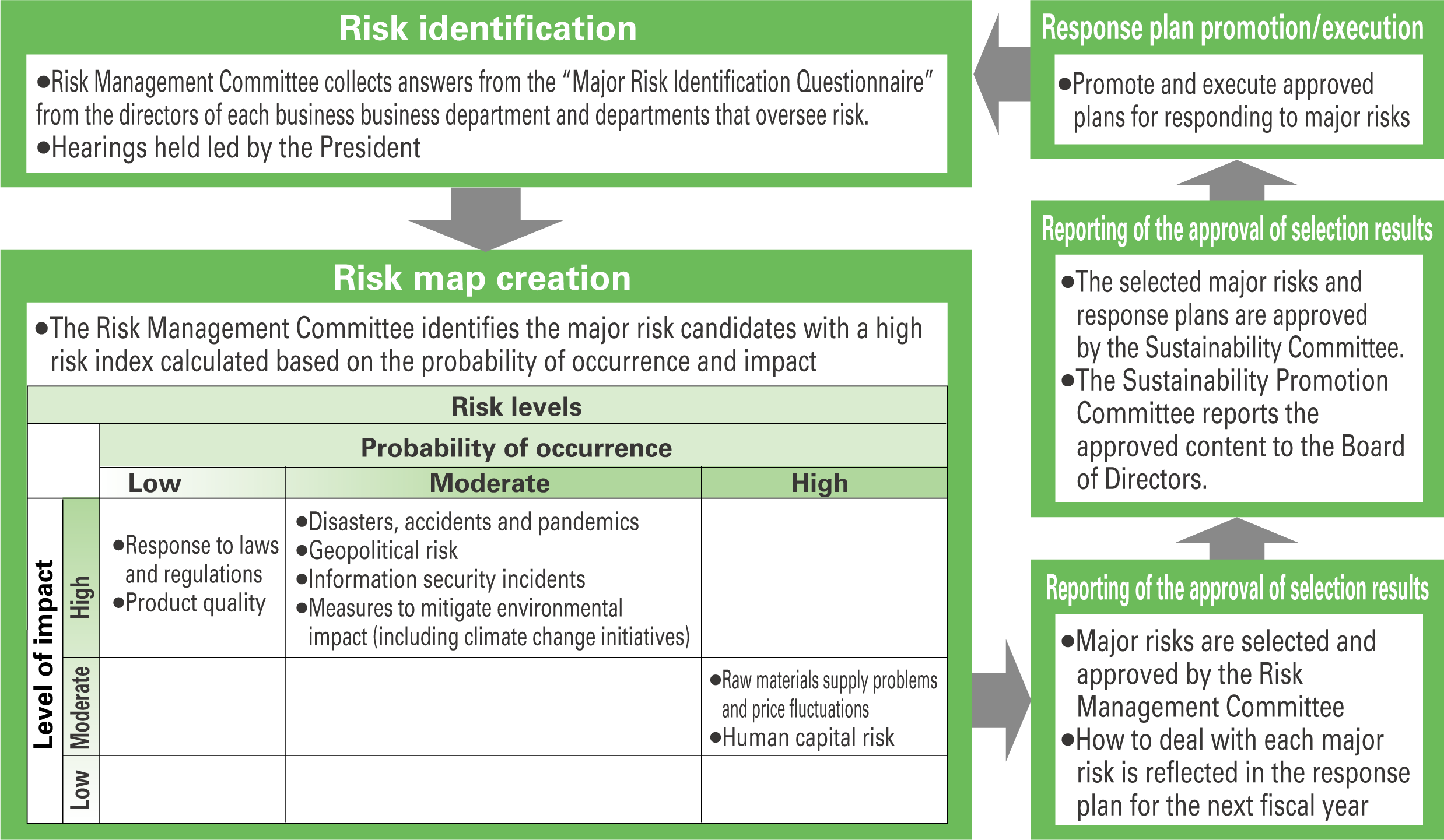
Major Risk Selection and Approval Process
The selection and approval of major risks in the Group is conducted once a year. The process is as follows.
●Guidelines for Selecting the Degree of Probability of Occurrence
| Levels | Guidelines for selecting the level of probability of occurrence | |
| Probability of occurrence | Low | Approximately once every 100 years to once every 10 years |
| Moderate | Approximately once every few years to once every year | |
| High | Twice or more each year | |
●Guidelines for selecting level of impact
| Levels | Guidelines for selecting the level of impact (If more than one of the following applies, select the item with the highest level of impact) | |||
| Monetary impact | Human life | Reputation | Impact on operations | |
| Level of impact Low |
to ¥50 million | Injuries or illnesses requiring medical attention occur | Resolved through routine daily management | Affects operations for a few days at one location only |
| Level of impact Moderate |
¥50 million to ¥1.0 billion |
Injuries or illnesses requiring hospitalization occur | Minor coverage (in a negative way) in conventional and online mass media Trust is partially diminished among business partners and consumers | Affects operations for several weeks at one location only Affects operations for multiple days at multiple locations |
| Level of impact High |
¥1.0 billion - | One or more deaths occur Numerous cases of injury and/or sickness occur |
Major coverage (in a negative way) in conventional and online mass media Trust is considerably diminished among business partners and consumers | Affects operations for several months at one location only Affects operations for multiple weeks at multiple locations |
Major Risk Content, Potential Impacts, and Responses
Based on the above-mentioned major risk selection process, the Group has identified the following major risks that could have a significant impact on the Groupʼs business, and by viewing these as opportunities and promoting responses, the Group will create value in the future.
The eight major risks selected in fiscal 2023 that must be addressed in fiscal 2024 are: (1) disasters, accidents, and pandemics, (2) geopolitical risk, (3) information security incidents, (4) measures to mitigate environmental impact (includes climate change), (5) compliance with laws and regulations, (6) product quality, (7) raw materials supply problems and price fluctuations, and (8) human capital risk.
Of these, the risks associated with climate change are (1) disasters, accidents and pandemics, (4) measures to mitigate environmental impact (including responses to climate change), (5) compliance with laws and regulations, and (7) raw material supply problems and price fluctuations.
| Risk | Details and potential impacts of risks | Handling and opportunities | ||||||
Disasters, accidents and pandemics
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
Opportunities
|
|||||||
Geopolitical risk
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
||||||||
Information security incidents
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
Opportunities
|
|||||||
Measures to mitigate environmental impacts
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
Opportunities
|
|||||||
Response to laws and regulations
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
Opportunities
|
|||||||
Product quality
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
Opportunities
|
|||||||
Raw materials supply problems and price fluctuations
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
Opportunities
|
|||||||
Human capital risk
|
Details
|
Responses
|
||||||
Impacts
|
The major risks listed above are not an exhaustive list of all risks faced by our Group, as other are other risks that are difficult to foresee. Please also refer to the Securities Report for information on individual risks and how we handle them, as well as opportunities.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Of the foreseeable disasters and accidents that could occur, we regard earthquakes; explosions, fires, and leaks, storm and flood damage; and pandemics as major emergencies. We prepare Business Continuity Plan (BCP) designed to ensure the continuity of business when such emergencies occur, and share these with our clients as needed. Thus far, we have implemented measures such as ensuring adequate inventories of products and raw materials, ensuring redundancy with our production systems, augmenting our supplies of spare parts, and systematizing our restoration structures. With the cooperation of our suppliers, we are also confirming BCP upstream in the supply chain and examining additional countermeasures, while expanding the introduction of a predictive anomaly management system based on AI and IoT technologies as a preventive measure against fires and explosions that could occur in our Group.
Our response to COVID-19 has included the establishment of a COVID-19 Emergency Taskforce and a countermeasures secretariat at our head office, which operated flexibly as we deliberated measures to be taken in response to the state of the contagion, such as issuing notices as appropriate. We also consider the operation of these two bodies in revising our Companywide COVID-19 Infection Countermeasures Manual as needed. We also referred to this manual in our work of formulating a response framework and action plan for each of our subsidiaries in consideration of the differences in laws, regulations and industry rules for the country in which each was located.
We recognize that the frequency with which disasters and incidents that we regard as major emergencies occur, as well as the magnitude and extent of their impacts, is changing every year as a result of advances in science and technology and the effects of climate change. As such, every year we verify the adequacy of our BCPs based on the latest information. Moving forward, we will continue to reassess our BCPs and provide training.
Topics More
- 2024/10/01 Sustainability Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. signed to the UN Global Compact
- 2024/02/01 Sustainability Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. announces its establishment of “Human Rights Policy for the Group of Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd.”
- 2023/10/31 Sustainability Integrated Report 2023 of Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd. has been issued.
- 2023/06/21 Sustainability Selected as an iSTOXX® MUTB Japan Platinum Carrier 150 Index
Email us about Sustainability
Inquiry